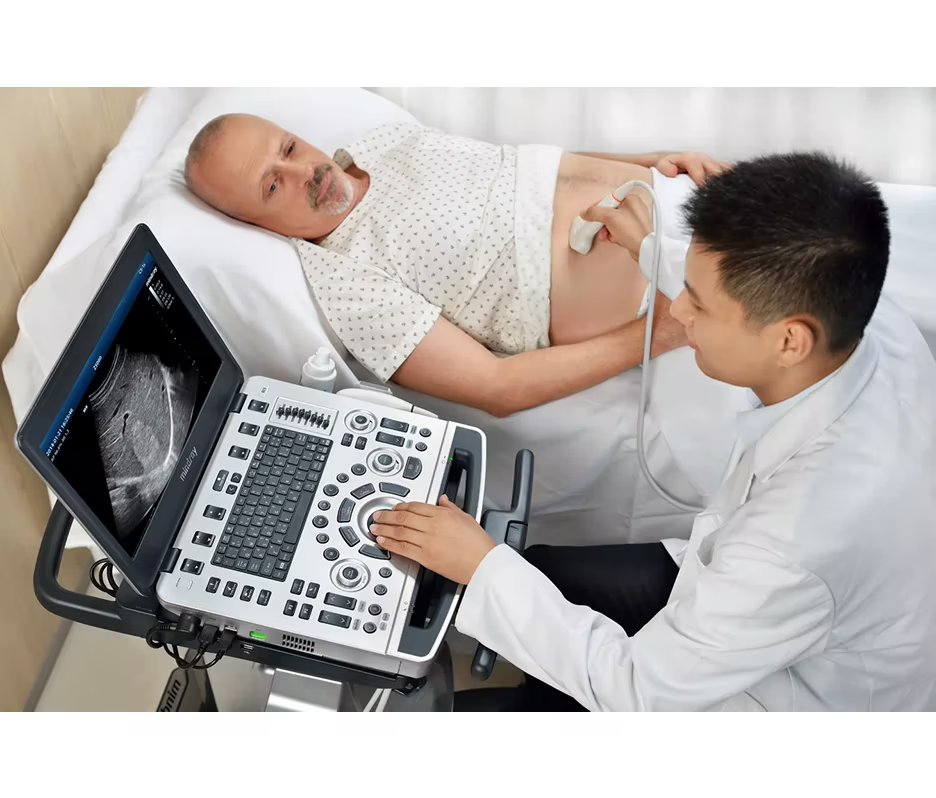
What is an Ultrasound Machine, and What is Its Operational Mechanism?
Ultrasound imaging is a term familiar to many individuals, as it is widely recognized in the medical field. There are numerous reasons why diagnostic ultrasound has become one of the most prevalent testing procedures utilized in healthcare.
Ultrasound scanning is so ubiquitous that virtually every medical testing facility is equipped with a diagnostic ultrasound machine. However, while many people are aware of what an ultrasound examination entails, few possess a comprehensive understanding of its operational principles.
What exactly is an ultrasound machine, and how does it function? This article will explore the fundamentals of ultrasound technology, its mechanisms, and the various types of ultrasound imaging devices available.
What is Medical Ultrasound Imaging?
Medical ultrasound imaging is a technique that employs sound waves to examine the internal organs of the body for diagnostic, testing, or therapeutic purposes. The sound waves penetrate the body and are transformed into ultrasound images that depict the condition and contours of fluids, soft tissues, and internal organs. This enables healthcare professionals to identify issues and formulate treatment plans.
Medical ultrasound imaging is instrumental for physicians in diagnosing conditions related to internal organs and identifying sources of inflammation or pain within the body.
Additionally, ultrasound imaging is the most frequently used testing method for monitoring fetal development in pregnant women.
This imaging technique utilizes ultrasound waves, which are high-frequency sound waves that are inaudible to the human ear.
What is the difference between Ultrasound and Sonography?
Many individuals conflate the terms ‘sonography’ and ultrasound, but it is important to recognize their distinctions.
As previously mentioned, ultrasound can serve both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. In its diagnostic capacity, it functions as an imaging technique, whereas in its therapeutic role, it does not produce images. Common therapeutic applications include the application of deep heat to specific soft tissue areas.