The Role of Ultrasound in Veterinary Medicine and Animal Care
Ultrasound technology has become an essential part of modern veterinary practice, offering a safe and efficient way to examine animals without surgery. Though many people associate ultrasound with human medicine—especially pregnancy—it plays a critical role in diagnosing and treating animals of all kinds, from household pets to livestock and exotic species.
Understanding Veterinary Ultrasound
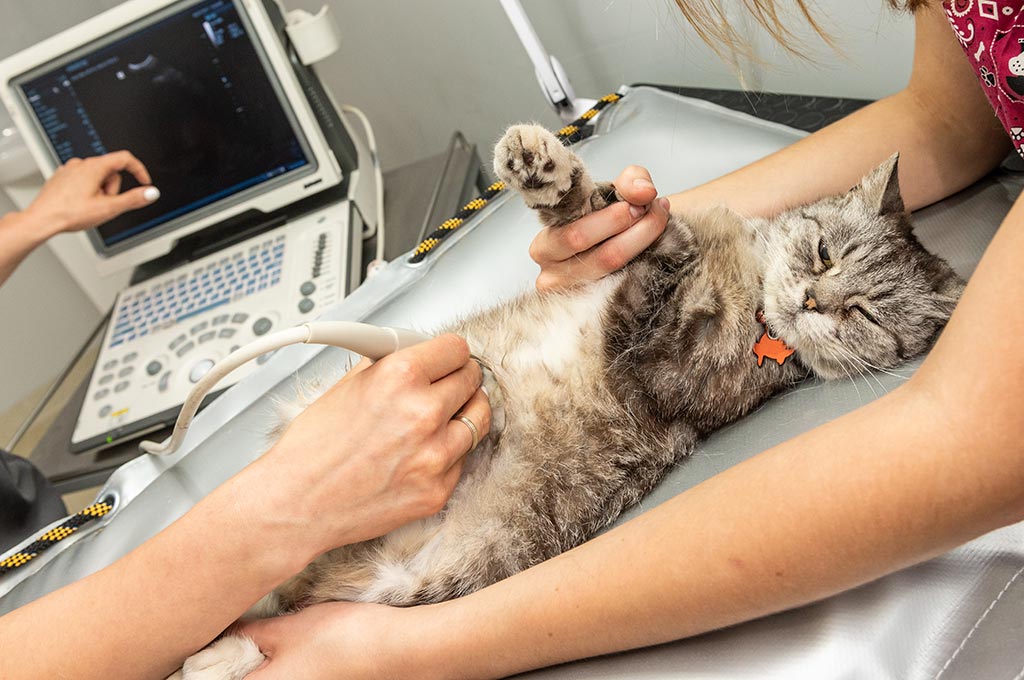
Ultrasound is a diagnostic imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to generate real-time images of the body’s internal structures. In animal care, this allows veterinarians to assess the condition of organs, soft tissues, and even blood flow without the risks associated with radiation or invasive procedures.
Unlike X-rays, which primarily capture images of dense materials like bones, ultrasound excels at visualizing soft tissue structures such as the liver, kidneys, bladder, and heart.
How Ultrasound Is Used in Animal Healthcare
1. Internal Diagnostics
When an animal presents with vague symptoms—such as lethargy, vomiting, or unexplained weight loss—ultrasound can help uncover the cause. It allows vets to identify abnormalities like tumors, inflammation, fluid accumulation, or blockages. This detailed internal view helps in making faster, more accurate diagnoses.
2. Reproductive Monitoring
Ultrasound is widely used in animal breeding and prenatal care. It enables early pregnancy detection, estimation of fetal age, and monitoring of fetal development. For breeders, this tool is especially valuable in managing the health and timing of litters or births.
3. Guided Procedures
Veterinarians often rely on ultrasound to assist in performing medical procedures with greater accuracy. For example, it’s commonly used to guide needle biopsies or fluid extractions, reducing risk and increasing the success rate of the intervention.
4. Cardiac Examinations
Specialized ultrasound techniques like echocardiography allow vets to closely examine the heart’s structure and function. This is particularly useful in diagnosing heart conditions in animals such as dogs and cats, where symptoms may not be immediately obvious.
5. Emergency Situations
In urgent care scenarios, ultrasound can quickly reveal internal injuries or complications following trauma, such as internal bleeding or organ damage. The ability to perform these assessments rapidly and without sedation is a major advantage in critical care settings.
Benefits of Using Ultrasound in Veterinary Medicine
- Non-invasive and painless – Ultrasound does not require incisions or recovery time.
- Radiation-free – It’s safe for animals of all ages, including those that are pregnant.
- Real-time results – Movement within the body, like heartbeat or fetal motion, can be observed immediately.
- Wide applicability – Useful across many species, from common pets to large farm animals and wildlife.
Applications Beyond Traditional Pets
Ultrasound isn’t limited to cats and dogs. It is increasingly used to monitor the health of birds, reptiles, small mammals, and even zoo animals. Portable ultrasound machines make it easier to perform scans on-site, which reduces stress for animals that can’t be easily transported to a clinic.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Veterinary Ultrasound
Technological innovations are making ultrasound more accessible than ever. Compact, handheld devices now allow veterinarians to conduct exams in the field or in remote locations. Some systems are also beginning to integrate artificial intelligence to enhance image interpretation, enabling quicker and more reliable diagnoses